






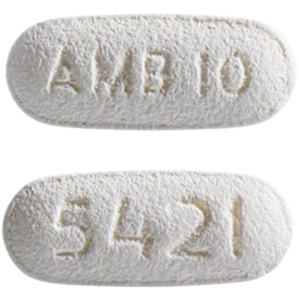

Experience the ease of managing your health with Onlinedeliveryrx.com Our online platform offers a seamless way to order your medication from the comfort of your home. Trust us for reliable service and timely delivery, ensuring your wellness is always within reach.
Email: support@onlinedeliveryrx.com
Call Us: +1 315 897 3886
909 E. Indigo Ct. Gilbert AZ 85298



